In today’s digital-first era, businesses are increasingly dependent on cloud computing for data storage, deployment of applications, and scalability of operations. But with greater flexibility comes greater responsibility. A well-defined cloud security policy is no longer a best practice; it has become a business necessity to protect sensitive information, meet compliance standards, and maintain customer trust.
The guide is based on practical experience in cloud security frameworks and policy audits, besides real-world cloud deployments across SaaS and enterprise environments. Whether you are a startup totally dependent on cloud software or an enterprise that is already developing a hybrid or multi-cloud environment, this guide should be useful for understanding, designing, and implementing proper cloud security policies that really work in practice.
What Are Cloud Security Policies?
A cloud security policy is a formal set of rules, regulations, and standards that prescribes how an organization secures its cloud systems, data, and services. This outlines clearly what is permitted, what is not, and the way in which cloud security controls are enforced across cloud environments.
You can think of it as the traffic rules for your cloud infrastructure. Without proper regulations, organizations will inevitably expose themselves to risks related to data breaches, misconfigurations, and compliance violations.
The best cloud security policies address the following:
- Cloud data protection and cloud data classification
- Access control and identity management in the cloud
- Approved cloud services, including SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS security
- Cloud incident response and recovery
- Cloud audit and compliance requirements
Why Cloud Security Policies Are Important
Cloud environments operate under a shared responsibility model, where the cloud service provider and the customer both have defined cloud security responsibilities. Without documented and enforced policies, security gaps appear, and attackers tend to exploit these gaps faster than organizations expect.
Key reasons cloud security policies matter:
- Protect sensitive data from breaches, leaks, and unauthorized access
- Ensure the CIA triad: confidentiality, integrity, and availability
- Meet cloud compliance requirements such as GDPR, ISO 27001, and NIST
- Reduce human error, the leading cause of cloud security incidents
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities across teams
In real-world cloud environments, one of the most common mistakes businesses make is assuming that all security is handled by the cloud provider. Cases have been observed where customer data was exposed due to misconfigured storage buckets because access policies were never reviewed after deployment.
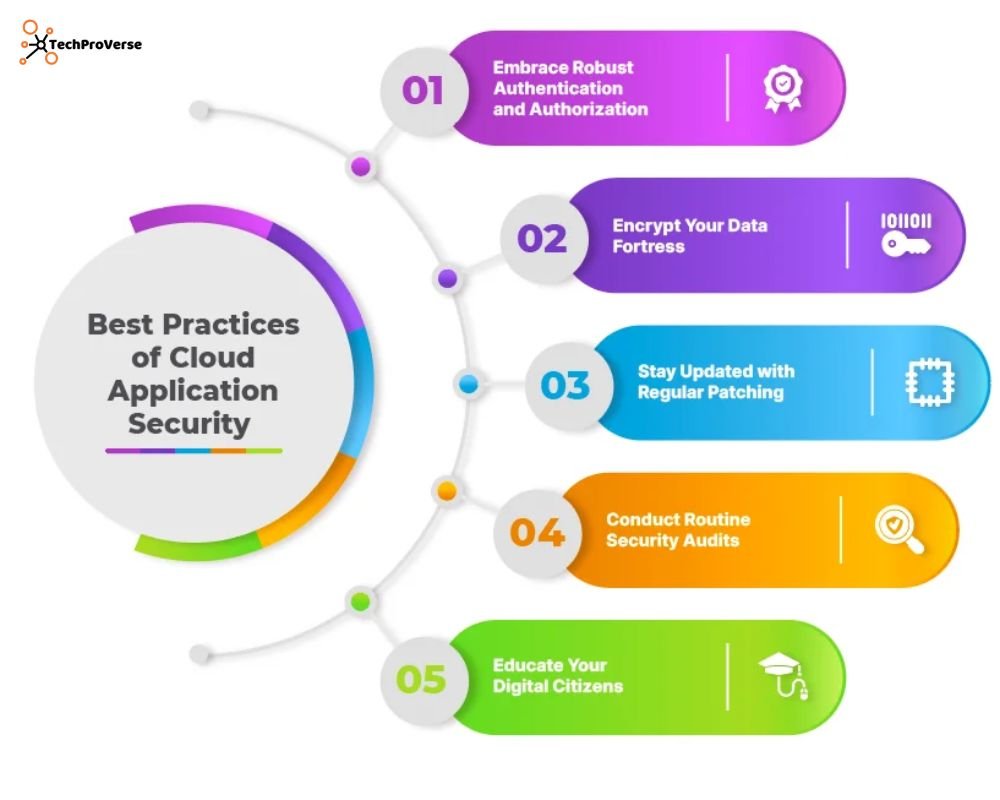
Key Components of Cloud Security Policies
A cloud security policy is not merely a document; it is a structured cloud security framework that aligns technology, people, and processes.
1. Cloud Governance Policy
A cloud governance policy defines approved cloud services, vendors, and usage rules. This ensures teams use only trusted platforms that meet both business and compliance requirements.
2. Cloud Data Protection
This component focuses on securing business data and includes:
- Cloud data classification (public, internal, confidential)
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Clearly defined data ownership and accountability
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Strong IAM policies include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Principle of least privilege access
4. Cloud Security Controls
Effective cloud security controls integrate technical and administrative safeguards such as:
- Firewalls and network segmentation
- Cloud monitoring and logging
- Regular security control assessment
Any cloud security policy that is not enforced through automation is likely to fail, as manual enforcement does not scale in modern cloud environments.
5. Incident Response and Recovery
This section explains how the incident response team (IRT) detects, contains, and recovers from cloud security incidents.
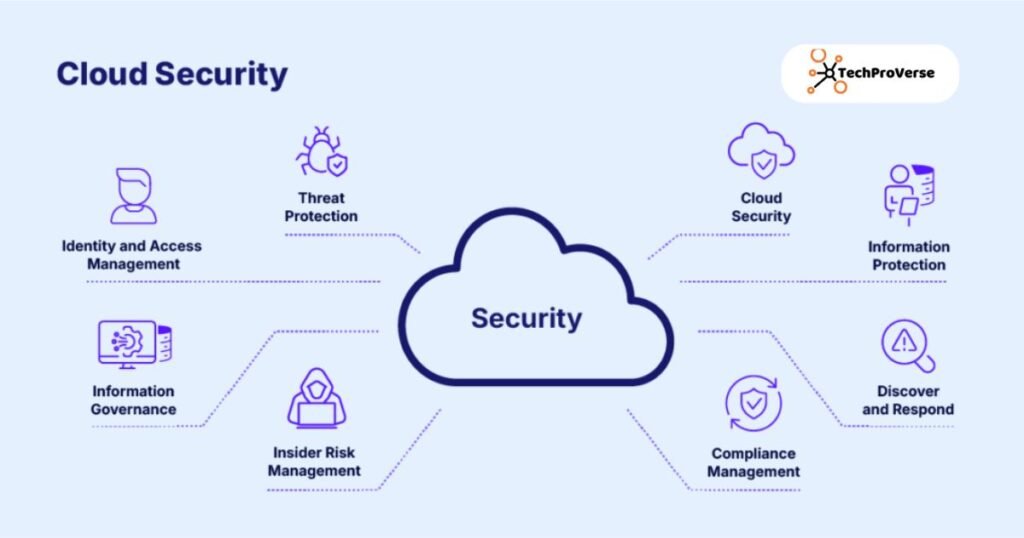
Common Cloud Security Policies
Different risks require different policies. Most organizations implement the following cloud security standards:
- Cloud access control policy
- Cloud data classification policy
- Cloud incident response policy
- Cloud compliance and audit policy
- Cloud infrastructure security policy
- Cloud service provider and SLA policy
Traditional IT Security vs. Cloud Security Policies
| Aspect | Traditional IT Security | Cloud Security Policy |
| Infrastructure | On-premises | Cloud-based (shared responsibility) |
| Access Control | Network-based | Identity-based (IAM) |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Policy Enforcement | Manual | Automated |
| Compliance Audits | Periodic | Continuous monitoring |
How to Create a Robust Cloud Security Policy
Creating an effective cloud security policy is not about copying a generic template; it’s about tailoring it to your specific needs. It requires alignment with business objectives and risk tolerance.
Step-by-step approach:
- Identify business goals and acceptable risk levels
- Understand cloud service models and security implications
- Map regulatory compliance and audit requirements
- Clearly define cloud security responsibilities
- Write policies in simple, actionable language
A structured cloud security policy template can expedite the process, but customization is crucial.
Steps to Implement Cloud Security Policies
Policies only create value when enforced.
Practical implementation steps:
- Conduct security awareness training for employees
- Enforce policies using cloud-native security tools
- Enable centralized cloud monitoring and logging
- Automate cloud policy enforcement where possible
- Review and update policies regularly
Roles and Responsibilities in Cloud Security Policy
Clear ownership improves accountability and incident response times.
Typical roles include:
- Cloud Security Manager – Oversees cloud security management
- IT/Admin Teams – Implement and maintain cloud security controls
- Compliance Officer – Manages cloud audit and compliance efforts
- Employees – Follow approved cloud usage policies
Risk Assessment and Security Controls in Cloud Environments
Proactive cloud risk assessment helps identify vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
Key activities include:
- Risk identification and mitigation
- Security control assessment
- Continuous vulnerability scanning
- Misconfiguration analysis
Incident Response and Recovery Planning
No cloud environment is risk-free. What matters most is response speed.
An effective cloud incident response plan includes:
- Incident detection and alerting
- Defined escalation paths
- Containment and remediation steps
- Security incident recovery process
- Post-incident review and improvements

Cloud Security Policies in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Managing security across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud adds complexity.
Best practices include:
- Standardizing cloud security standards
- Centralizing cloud security management
- Applying cloud governance policies consistently
- Using unified monitoring and logging tools
Cloud Security Policy Best Practices
- Keep policies clear, practical, and enforceable
- Enforce least privilege access
- Automate compliance checks
- Review and update policies regularly
- Align with cloud security frameworks such as NIST
Common Cloud Security Policy Implementation Challenges
Organizations often face:
- Limited visibility across cloud services
- Poor policy enforcement
- Employee resistance or lack of awareness
- Uncontrolled cloud adoption
Cloud Security Policy Examples and Templates
A strong cloud security policy template includes:
- Purpose and scope
- Approved cloud services
- Cloud data protection requirements
- Cloud access control rules
- Incident response procedures
- Enforcement and non-compliance handling
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a cloud security policy?
A cloud security policy defines controls to protect cloud data, applications, and infrastructure.
2. What are the 5 pillars of cloud security?
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Privacy, and Compliance.
3. What are the 4 C’s of cloud security?
Compliance, Configuration, Control, and Change management.
4. What is the ISO cloud policy?
A set of guidelines based on ISO/IEC 27001/27017 standards for securing cloud services and managing risks.
5. What are the three security policies?
Acceptable Use Policy, Access Control Policy, and Data Protection Policy.
Related Headings:
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
Zero-Day Vulnerability News 2025: Urgent Threats, Active Attacks & Patch Alerts
How to Detect Phishing Attacks
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
5 Best ChatGPT Alternatives
Best Antivirus Software for PC 2025
Beginner’s Guide to Blue Team Cybersecurity
Conclusion:
An effective cloud security policy is the foundation of secure cloud computing. It protects sensitive data, ensures compliance, and brings clarity across teams. More importantly, it enables businesses to scale confidently without unnecessary risk.
Recommendation:
Keep cloud security policies simple, practical, and continuously evolving. Cloud security is an ongoing journey, and investing in strong policies today safeguards your business tomorrow.

Welcome to TechProVerse! I’m Abdullah, a WordPress and front-end developer, as well as an SEO researcher with 1.5 years of experience. I help websites get built, optimized, and rank higher on Google. Let’s achieve more together!
















