A Complete Guide to Understanding ML vs DL Differences
Understanding machine learning vs deep learning is now essential because both technologies shape how modern digital systems think and learn. Many people also confuse them with artificial intelligence, so this guide explains everything in simple English. You will understand the difference between machine learning and deep learning, how each one works, where they are used, and how to choose between ML and DL based on your project. This comparison also includes AI ML DL differences, real-world use cases, accuracy comparisons, dataset needs, training time, interpretability, neural networks, and more.
Artificial intelligence has grown fast in recent years. Today, “AI powering modern applications” is common in smartphones, search engines, cars, healthcare, entertainment, and security. Behind these systems, “machine learning vs deep learning drive automation” and help machines learn from data. But both work differently, and understanding these differences helps you build better tools, apps, and business systems.
Related Headings:
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
ChatGPT vs Google Gemini: Which AI Chatbot Will Win
Best Antivirus Software for PC
5 Best ChatGPT Alternatives
Top Free Deepfake AI Tools You Can Try Today
What is Machine Learning? (ML Explanation)
Machine learning is a branch of AI where the system learns patterns from data and improves with experience. The core idea is that “machine learning requires human intervention”, mainly because machine learning needs manual feature engineering. Humans must decide which features or patterns the model should learn. This process is known as feature extraction in machine learning and is very important for ML models.
Another key point is that “machine learning works with smaller datasets”. ML is perfect for projects where data is limited, structured, or easy to organize. It performs well on structured data like spreadsheets or CSV files. ML models such as linear regression, decision trees, and random forests are popular examples. These examples of machine learning models are widely used in finance, marketing, business analytics, fraud detection, and predictive analytics with machine learning.
Machine learning also supports supervised vs unsupervised vs reinforcement learning, giving developers several ways to train models depending on the problem. ML is also easier to understand because the model’s reasoning is visible, making the interpretability of ML vs DL much better. Many companies still prefer ML for transparency, cost-effective training, and faster development cycles.
What is Deep Learning? (DL Explanation
Deep learning is an advanced form of machine learning that works using layered neural networks. The core principle is that “deep learning uses artificial neural networks”, which behave like the human brain. Because of these layers, “deep learning models learn automatically from raw data”, meaning developers do not need to manually define features. This automatic learning process means deep learning learns features automatically, reducing the need for manual work.
Deep learning also uses neural networks in deep learning such as CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, GANs, and even transformers. These are powerful examples of deep learning models designed for different use cases. For example, CNNs are used for computer vision tasks (CNN) such as image recognition deep learning, while RNNs and LSTMs help with sequential data processing (RNN, LSTM) and speech recognition deep learning.
However, “deep learning needs large datasets and high compute power” because the models have many layers. DL also requires GPUs because GPU vs CPU in deep learning makes a huge difference. GPUs are much faster at parallel processing, which helps reduce the training time. But DL often remains a black box deep learning system, meaning it is harder to understand how the model makes decisions.
Deep learning powers many modern technologies, including autonomous vehicles deep learning, face recognition, robotics, and advanced natural language processing deep learning.
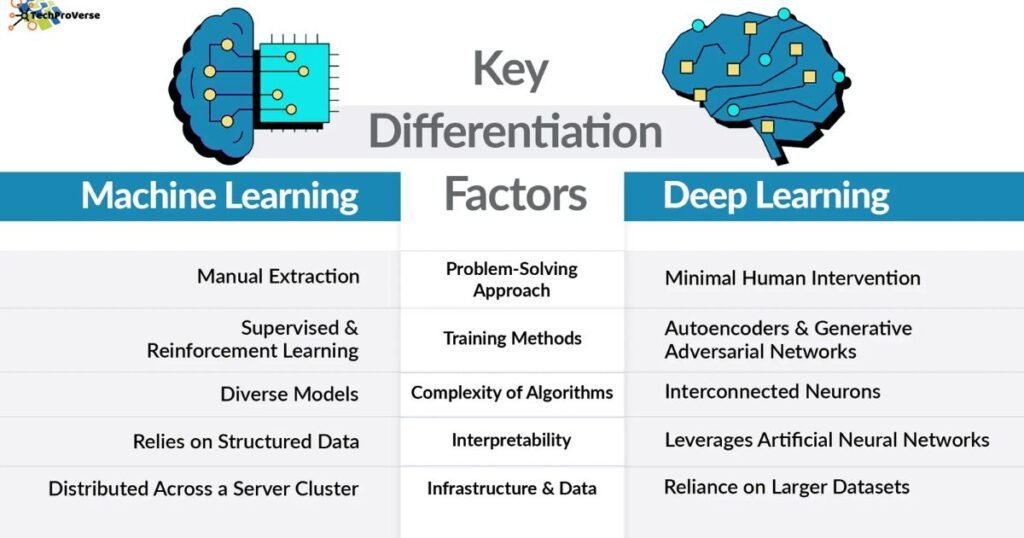
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning: Key Differences Explained
The machine learning vs deep learning differences become clearer when comparing how they work, how much data they need, and what kind of problems they solve. ML usually needs simpler data and human guidance. In contrast, DL can learn directly from raw images, text, audio, and video because of neural networks.
ML works better with small dataset vs big dataset situations, especially when data is limited. DL requires massive training data and more computational resources. ML offers faster results and easier debugging. DL is harder to interpret but more accurate for complex pattern recognition tasks.
Understanding these artificial intelligence vs machine learning vs deep learning levels helps beginners see the relationship: AI is the big umbrella, ML is a subset of AI, and DL is a subset of ML.
ML vs DL Comparison (Simple and Clear)
| Feature | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Engineering | “machine learning needs manual feature engineering” | “deep learning learns features automatically” |
| Human Intervention | High | Low |
| Dataset Size | “machine learning works with smaller datasets” | “deep learning needs large datasets and high compute power” |
| Model Structure | Simple algorithms | Multi-layer neural networks |
| Processing Power | CPU is enough | Needs GPU |
| Interpretability | Easy to understand | black box deep learning |
| Training Time | Faster training time in machine learning | Longer training |
| Accuracy | Lower for complex tasks | Higher accuracy of deep learning models |
| Data Type | structured data like spreadsheets or CSV files | unstructured data such as images, audio, and text |
This table shows the ML vs DL comparison and helps you understand how these two learning techniques solve different types of problems.
How Machine Learning Works (With Algorithms and Examples)
Machine learning follows a simple process. First, data is collected and cleaned. Then features are selected manually. This is why feature extraction in machine learning plays such an important role. After feature selection, models such as linear regression, SVM, naive Bayes, random forest, or k nearest neighbors are trained. These are common machine learning algorithms.
ML models are good at handling business tasks, banking analytics, customer segmentation, risk prediction, medical diagnosis, and recommendation systems machine learning solutions. These systems learn from user activity and predict behavior patterns.
Many companies choose ML when they need transparency or faster development. ML is also great for smaller teams or startups because training the models does not require expensive machines.
How Deep Learning Works (Neural Networks, CNN, RNN, GAN, Transformers)
Deep learning works by passing data through multiple neural network layers. Each layer learns deeper and more abstract features. That is why types of neural networks such as CNN, RNN, LSTM, GAN, and transformers exist.
CNNs help with computer vision tasks (CNN) like face detection, traffic sign identification, and image recognition deep learning. RNNs and LSTMs help understand text or audio and are used in sequential data processing (RNN, LSTM) tasks. GANs generate new images, videos, or voices, while transformers help in modern natural language processing deep learning tasks like ChatGPT.
Deep learning is used in medical imaging, fraud detection, voice assistants, smart home devices, robotics, and autonomous vehicles deep learning. Because DL learns automatically from raw data, it performs better in situations where patterns are complex or hidden.
Real-World Applications of ML vs DL
Machine learning is widely used in business forecasting, pricing models, credit scoring, marketing analytics, and fraud detection. These real world applications of ML help companies make better decisions faster.
Deep learning is used in vision systems, speech recognition, medical imaging, robotics, and content creation tools. These real world applications of deep learning are more accurate when dealing with complex patterns or huge datasets.
Both machine learning vs deep learning support “reinforcement learning for recommendations”, especially in platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and e-commerce stores.
How to Choose Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Choosing between these two depends on your data, computing power, time, and accuracy needs. When data is limited, or you need transparency, ML works best. When accuracy is more important than interpretability, DL is the right choice. This is why experts always say “choosing between ML and DL based on data size” helps you pick the right technology.
ML offers faster results, easier debugging, and cheaper training. DL provides higher accuracy, handles complex tasks, and works with images, audio, and text automatically. But DL needs GPUs, more data, and more time to train.
Related Headings:
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
ChatGPT vs Google Gemini: Which AI Chatbot Will Win
Best Antivirus Software for PC
5 Best ChatGPT Alternatives
Top Free Deepfake AI Tools You Can Try Today
Conclusion: Machine Learning vs Deep Learning Which Is Better?
In the end, the decision between machine learning vs deep learning depends on your project. ML is better for small datasets, low budget systems, business predictions, and transparent decision-making. Deep learning is better for image, audio, text, and video processing, especially when accuracy matters more than speed. Both technologies fall under AI, and combining them gives powerful results.
Understanding these machine learning vs deep learning differences helps you build better apps, smart tools, and modern digital systems.
FAQs
1. What are the key differences between machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning relies on manual feature engineering, while deep learning uses neural networks to learn automatically from raw data and works better with large datasets.
2. What is the primary distinction between ML and DL?
ML needs human-designed features, but DL extracts features automatically using multi-layer neural networks.
3. When should I use ML vs DL?
Use ML for small datasets and faster training; use DL for complex tasks like images, speech, and large-scale unstructured data.
4. Is ChatGPT deep learning or machine learning?
ChatGPT is a deep learning model because it uses transformer-based neural networks.
5. What are the 4 types of machine learning?
The four types are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
6. Is DL harder than ML?
Yes, deep learning is harder because it requires more data, higher computational power, and more complex model architectures.

Welcome to TechProVerse! I’m Abdullah, a WordPress and front-end developer, as well as an SEO researcher with 1.5 years of experience. I help websites get built, optimized, and rank higher on Google. Let’s achieve more together!