What is a Zero-Day Vulnerability? (Simple Explanation)
A zero-day vulnerability is an unseen flaw in software or hardware that is first discovered by the attackers before the vendors become aware. That makes it super dangerous, as those types of flaws can be exploited in the wild while users are unaware. Following zero-day vulnerability news helps companies and individuals find out how a critical zero-day flaw happens in a flash across popular apps, operating systems, and cloud platforms in the United States of America.
These are the types of flaws that generally create a rush to release emergency security patches, as bad guys waste little time. Attacks can leverage a zero-day in near real-time, and generally long before a patch is released by vendors, developed, or even deployed. Understanding the difference between a zero-day vulnerability and vs known vulnerability is important for reducing attack surface exposure and strengthening defenses before malicious activity occurs.
Rearmost Zero-Day Vulnerability News & Active pitfalls of the moment
Active Zero-Day Exploits Targeting Major Platforms
Every week, new zero-day vulnerabilities affect Microsoft, Apple, Google, Linux, and major cloud platforms. Many of these flaws are exploited before patches are available, creating chaos for U.S. organizations. Security advisory updates often confirm these vulnerabilities, helping IT teams prioritize urgent mitigation.
Attackers often use evidence of exploit chain activity to link multiple flaws together and further advance into networks. The zero-day vulnerability news weekly report provides an easy way for organizations to keep track of high-severity CVE vulnerabilities to proactively respond. Critical industries such as healthcare, finance, and government are most exposed.
Emergency Security Patches Released Today
Vendors release zero-day patch updates outside normal schedules when dangerous flaws are discovered. These updates provide urgent instructions for mitigating threats vulnerability disclosed by researchers only hours earlier. Companies following emergency mitigation steps can prevent large-scale exploitation.
| CVSS Score | Severity Rating | Risk Level |
| 9.0–10 | Critical | Highest priority |
| 7.0–8.9 | High | Fast action required |
| 4.0–6.9 | Medium | Fix soon |
| 0–3.9 | Low | Minimal impact |
Prompt patching reduces the risk of zero-day malware attacks, which can spread rapidly across Windows, Android, and iOS devices.
Zero Days Exploited in the Wild This Week
Security teams monitor zero-day exploit news to identify vulnerabilities that attackers actively use. Reports often include proof-of-concept exploit details before companies have a chance to patch systems. This week’s zero-day attack reports reveal flaws in browsers, mobile devices, VPN appliances, and cloud platforms.
Attackers often chain minor flaws to bypass defenses. Analysts observe exploit chain activity that lets intruders move deeper into networks. Automated tools quickly exploit unpatched systems, making real-time monitoring essential.
New High-Severity Zero Day Bugs (CVSS 9.0+)
The U.S. tech sector regularly sees dangerous zero-day vulnerabilities with CVSS 9.0+ ratings, allowing remote code execution without user action. These flaws impact routers, browsers, and enterprise software, creating significant attack surface exposure.
When vendors release patches, these flaws are often exploited before the patch is available, highlighting delays in the vulnerability disclosure timeline. Organizations that act quickly can prevent major breaches caused by high-risk bugs.
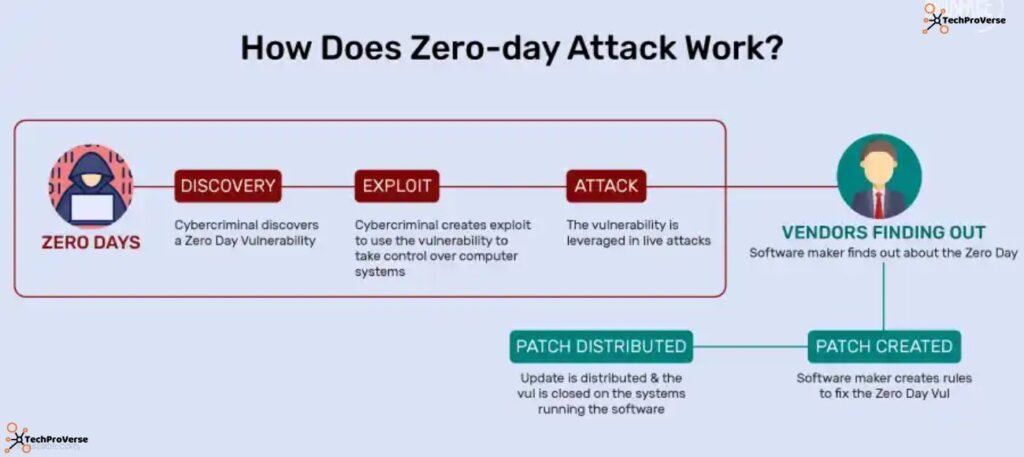
Recently Patched Zero-Day Vulnerability News (Vendor Updates)
Microsoft Zero Day Fixes
Microsoft zero-day updates address flaws in Windows, Office, and Exchange. Many vulnerabilities are disclosed by researchers after real-world exploits. The company provides vendor advisory and patch timeline details to help enterprises apply updates promptly.
These updates often fix vulnerabilities showing exploit chain activity evidence, where attackers escalate privileges. Microsoft urges users to enable auto-updates, reducing risk from dangerous zero-day vulnerabilities.
Google Chrome & Android Zero Day Updates
Google releases urgent Google Chrome zero-day alerts for flaws affecting browsers and Android. Attackers exploit these bugs to compromise millions of devices across the U.S. The company’s collaboration with bug bounty and coordinated disclosure programs helps catch high-risk vulnerabilities early.
Security advisory updates guide users to patch quickly, mitigating zero-day bug Android iOS threats before widespread attacks.
Apple iOS & macOS Zero Day Patches
Apple security patch notes address vulnerabilities exploited by hackers targeting journalists, executives, or political figures. These updates include Safari and kernel fixes to block spyware and prevent unauthorized access.
Apple works with global researchers to track indicators of compromise (IOCs) for zero-day and prevent exploit chain activity from compromising devices.
Open-Source & Linux Zero Day Vulnerabilities
Open-source zero-day vulnerabilities affect widely used Linux distributions, libraries, and container engines. Because Linux supports critical U.S. infrastructure, a single flaw can impact thousands of organizations. Researchers often report these issues through a vulnerability disclosure timeline, allowing fast mitigation.
Failing to patch quickly allows attackers to deploy zero-day malware attacks, highlighting the need for continuous updates and monitoring.

Major Zero-Day Attacks That Made Headlines
State-Sponsored Exploits & APT Groups
Many times, APT groups leveraging zero-days conduct state-sponsored cyber-attacks on the U.S. defense, energy, and technology sectors. Their operations use exploit chain activity to remain undetected for months, stealing sensitive data or disrupting systems.
Real-time monitoring via real-time threat intelligence shows how these groups exploit critical zero-day flaws to infiltrate networks globally.
Ransomware Gangs Using Zero-Day Exploits
Criminal organizations, called ransomware gangs using zero day exploits, use zero-day exploits to infiltrate corporate networks and encrypt vital data. Underground marketplaces provide access to dangerous zero-day vulnerabilities, allowing for rapid exploitation.
Case studies show hospitals, universities, and manufacturers losing millions due to attackers leveraging critical zero-day exploits.
Spyware & Surveillance Zero Days
Spyware developers rely on newly discovered zero-day bugs to monitor targets stealthily. Some campaigns affect journalists or political figures. Analysts review proof-of-concept exploit details and exploit chain activity evidence to track malicious behavior.
Many victims discover breaches only through real-time threat intelligence, demonstrating the importance of proactive monitoring.
Cloud Platform Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Cloud environments face trending cybersecurity vulnerabilities as companies migrate systems online. Zero-day attack examples show how a single flaw in AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud can compromise vast data sets.
Researchers employ automated threat hunting for zero days to detect intrusions early and prevent large-scale data theft.
How Security Researchers Discover Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Researchers use fuzzing, reverse engineering, and code audits to detect zero-day exploits 2025 before attackers. Many discoveries come via bug bounty and coordinated disclosure programs, which follow a structured vulnerability disclosure timeline.
Integration of threat intelligence feed data helps detect vulnerabilities exploited by threat actors, activating the incident response playbook for zero days to prevent full-scale breaches.

How to Protect Against Zero-Day Attacks (Practical Guide)
Enable Auto-Updates Across All Devices
Automatic updates help close critical zero-day flaws immediately. Many breaches occur because users delay patching, increasing attack surface exposure. Real cases show attackers exploiting before a patch is available within minutes.
Keeping systems current minimizes risks from dangerous zero-day vulnerabilities across Windows, Android, and iOS devices.
Use EDR & AI-Powered Threat Detection
Modern zero-day protection tools use AI to detect abnormal activity even without a patch. They provide endpoint security zero zero-day protection, and allow fast remediation.
Machine learning identifies exploit chain activity evidence in real-time, supporting detection and response best practices during active incidents.
Monitor Threat Intelligence & Advisories
Organizations track zero-day vulnerability updates through CISA, US-CERT, and cybersecurity services. Alerts often include indicators of compromise (IOCs) for zero-day, showing flaws and vulnerabilities disclosed by researchers or actively exploited.
Following these advisories ensures teams can implement zero-day vulnerability mitigation steps effectively.
Adopt Zero Trust Security Framework
Zero Trust verifies all access requests, reducing exposure to critical zero-day flaws. This approach complements how to protect against zero-day attacks, adding multiple defensive layers. Many U.S. organizations combine Zero Trust with automated threat hunting for zero days to maximize resilience.
Zero Day Vulnerability News: Frequently Asked Questions
What, in simple words, is a zero-day vulnerability?
It’s a zero-day vulnerability that nobody has patched to date, which allows attackers to get into systems undetected. Following zero-day vulnerability news helps organizations understand how these critical zero-day flaws can spread rapidly and pose serious risks.
Who did the zero-day attack?
It varies; sometimes APT groups exploiting zero days are the cause of breaches, while other times ransomware gangs using zero-day exploits are responsible. Monitoring real-time threat intelligence helps track attackers and prevent further compromise.
What is the most famous zero-day vulnerability?
Some examples include Stuxnet, Pegasus spyware, and SolarWinds-related flaws, all reported in global zero-day attack reports. These dangerous zero-day vulnerabilities demonstrate the importance of timely zero-day patch updates and zero-day protection tools.
What is the best solution for a zero-day attack?
The most effective defense combines Endpoint Security Zero Day Protection, enabling updates promptly, monitoring security advisory updates, and following zero-day vulnerability mitigation steps. These measures reduce attack surface exposure and limit exploit chain activity risks.
Which companies are most commonly affected by zero days?
Organizations within technology, healthcare systems, finance, and government are the most targeted due to high attack surface exposure. Following threat intelligence feed integration and staying updated on zero-day exploits in the wild helps mitigate these threats.
Related Headings:
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
ChatGPT vs Google Gemini: Which AI Chatbot Will Win
Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP): Complete Guide in 2025
How to Detect Phishing Attacks
How to Protect Your Data Online: Complete Guide for 2025
Best Antivirus Software for PC 2025
Cybersecurity Compliance: A Complete Guide for Modern Tech Businesses
Beginner’s Guide to Blue Team Cybersecurity
Final Thoughts: Keeping Up to Date with Zero-Day Vulnerability News
U.S. users and businesses must stay updated on zero-day vulnerability news. Leveraging real-time threat intelligence, applying emergency security patch updates, and monitoring security advisory updates help reduce risks. With newly discovered zero-day threats appearing every week, vigilance remains essential. Understanding how zero-day exploits work ensures systems remain secure in an ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.

Welcome to TechProVerse! I’m Abdullah, a WordPress and front-end developer, as well as an SEO researcher with 1.5 years of experience. I help websites get built, optimized, and rank higher on Google. Let’s achieve more together!
















